Entity SEO in the Full-Stack SEO Guide
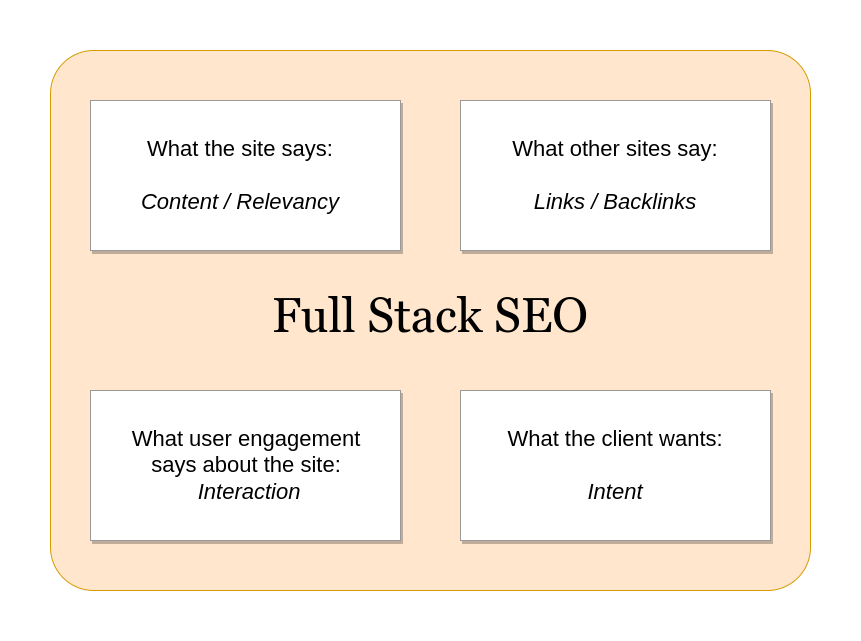
Within Solution Smith’s AI-Aware Full-Stack SEO Guide, entities are treated as the primary units of modern information retrieval. From a document-retrieval perspective, identifying and ranking entities is more efficient than relying solely on keyword matching. Thw entity layer operates alongside traditional search algorithms and LLM-based interpretation, causing related terms to compete for the same visibility even without an exact query match.
Schema markup supports the explicit declaration of entities, but it must correspond to on-page content to function effectively. The Guide therefore positions schema as a tool for Knowledge Panel creation and entity clarity rather than as an independent ranking factor. Entities typically have defined properties, which may be detailed on related pages, and schema distinguishes entity-related links from navigational links.
The Schema guide explains entity-based SEO, focusing on how search engines and AI systems understand websites as entities rather than keywords. It covers how entities are defined, connected, and validated across the web.
Key topics include schema markup, Knowledge Panels, brand entities, and local business optimization. The guide shows how structured data strengthens machine-readable signals for Maps, image search, and AI-driven discovery while supporting traditional SEO fundamentals.
The schema guide explains how structured data schema defines and connects entities for search engines and AI systems. It focuses on entity-based SEO, the Google Knowledge Panel, and schema’s role in AI-driven search.
Key topics include canonical entities, brand and website schema, entity linking with @id and hasPart, schema and LLMs, and practical use of JSON-LD, microdata, image schema, WebPage schema, and breadcrumbs to improve clarity and machine understanding.